What are Network Fees?
Understanding Cryptocurrency Network Fees
Network fees, also called transaction fees, are charges that users must pay to perform transactions on a cryptocurrency network.
These fees are essential for several reasons:
-
Rewards for Miners/Validators: Network fees are a way to incentivize miners (in Proof-of-Work systems like Bitcoin) or validators (in Proof-of-Stake systems like Ethereum 2.0) for their role in processing and confirming transactions.
-
Network Security: By incentivizing miners and validators, network fees help maintain the security and integrity of the blockchain. Without these fees, there would be less motivation to participate in the network, making it more vulnerable to attacks.
-
Transaction Priority: During network congestion, users can pay a higher fee to have their transactions prioritized. This creates a competitive market where users have an option to get their transactions confirmed quickly, and thus gives further incentive to the miners and validators.
Examples of Network Fees
- Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin transactions are processed by miners who solve complex mathematical problems. The fees on Bitcoin are measured in satoshis (the smallest unit of Bitcoin). Higher fees can lead to faster transaction confirmations, especially during periods of high demand.
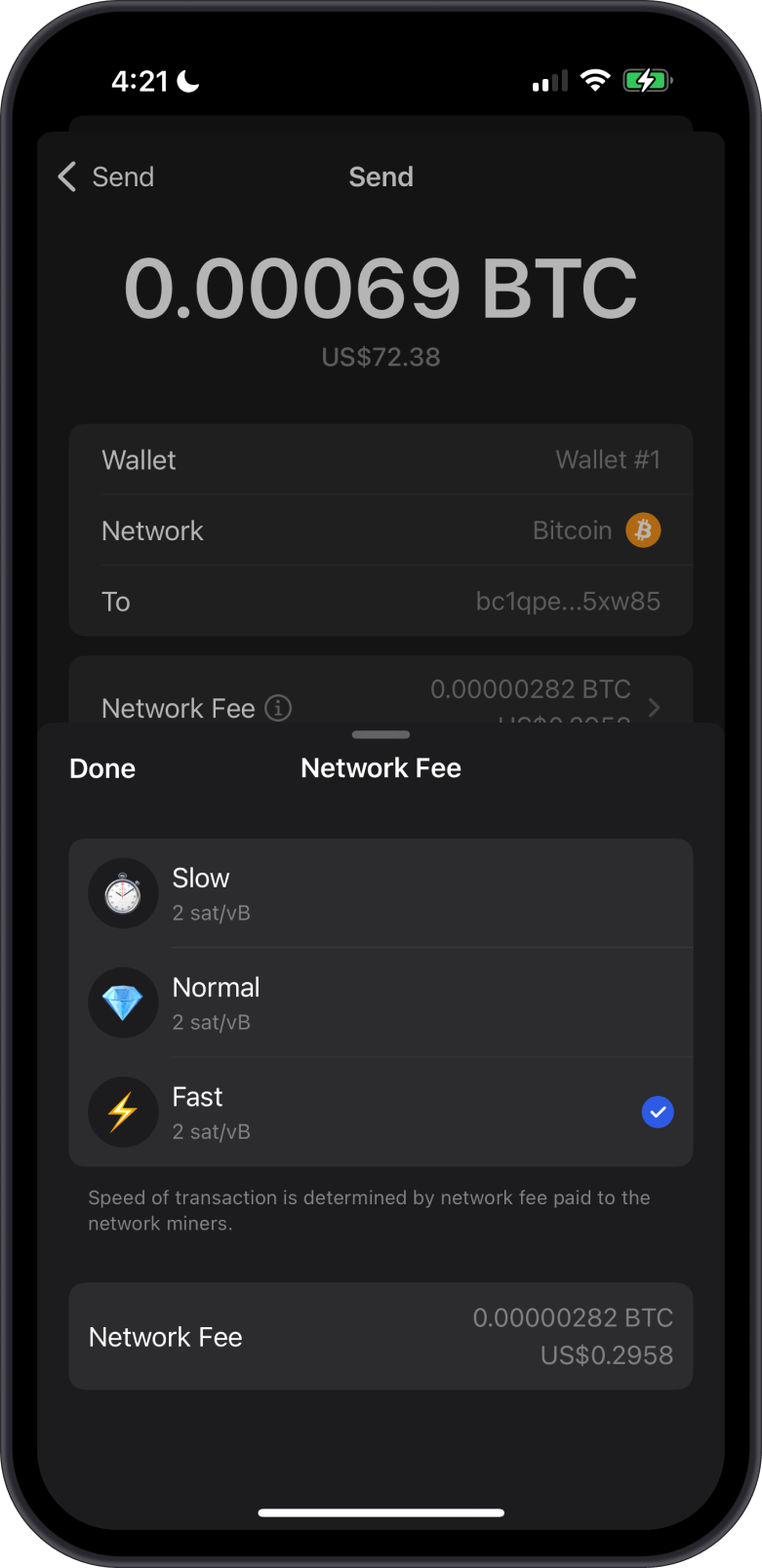
Learn more about Bitcoin and network fees.
- Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum uses the term "gas" to measure the computational effort required to process transactions and smart contracts. Gas fees are paid in ETH and can vary significantly based on network activity.
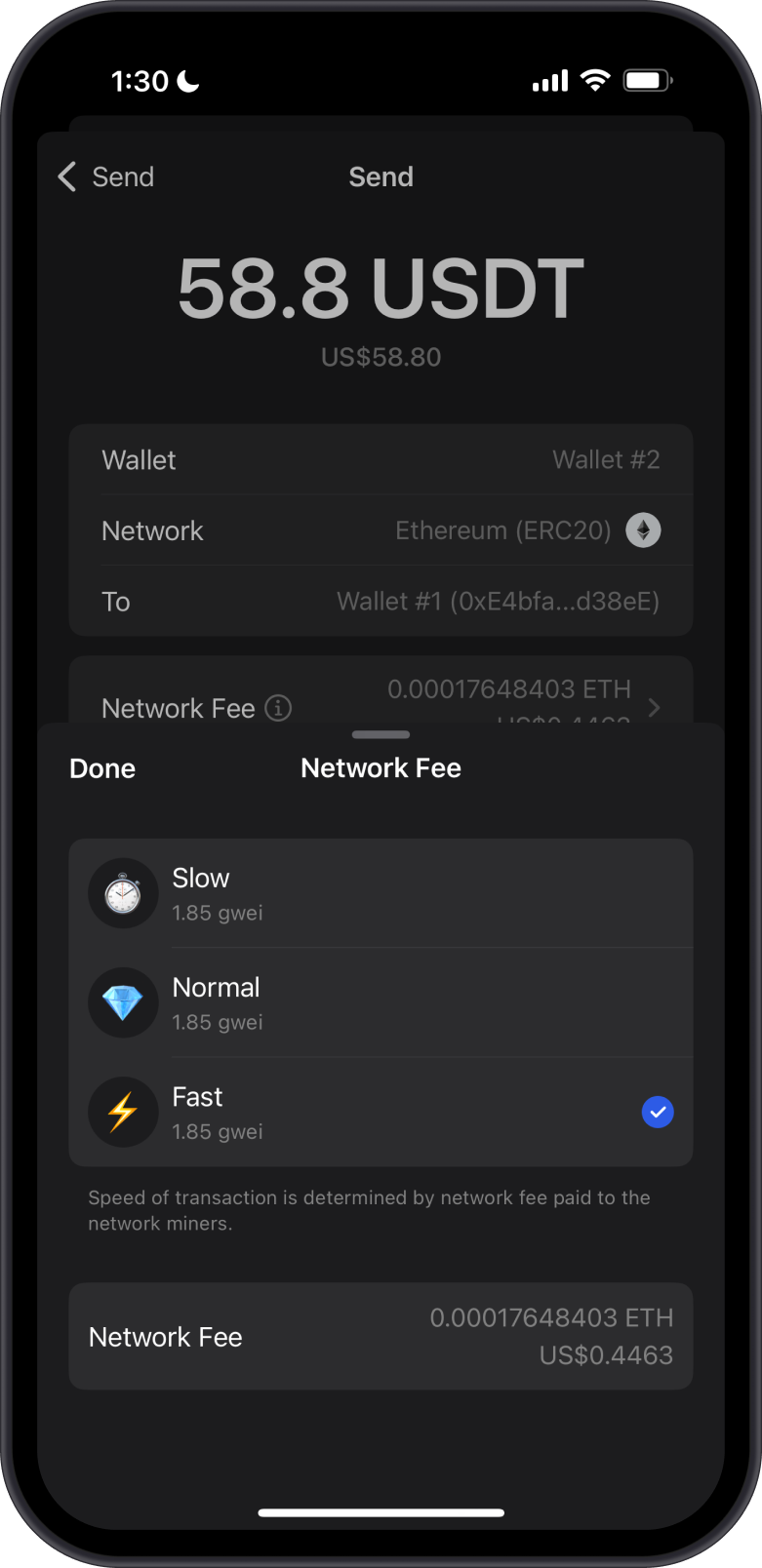
Learn more about Ethereum and network fees.
- Solana (SOL)
Solana uses its own Proof of History (PoH) consensus to achieve high throughput and low transaction costs. Solana's network fees are very low compared to other major blockchains.
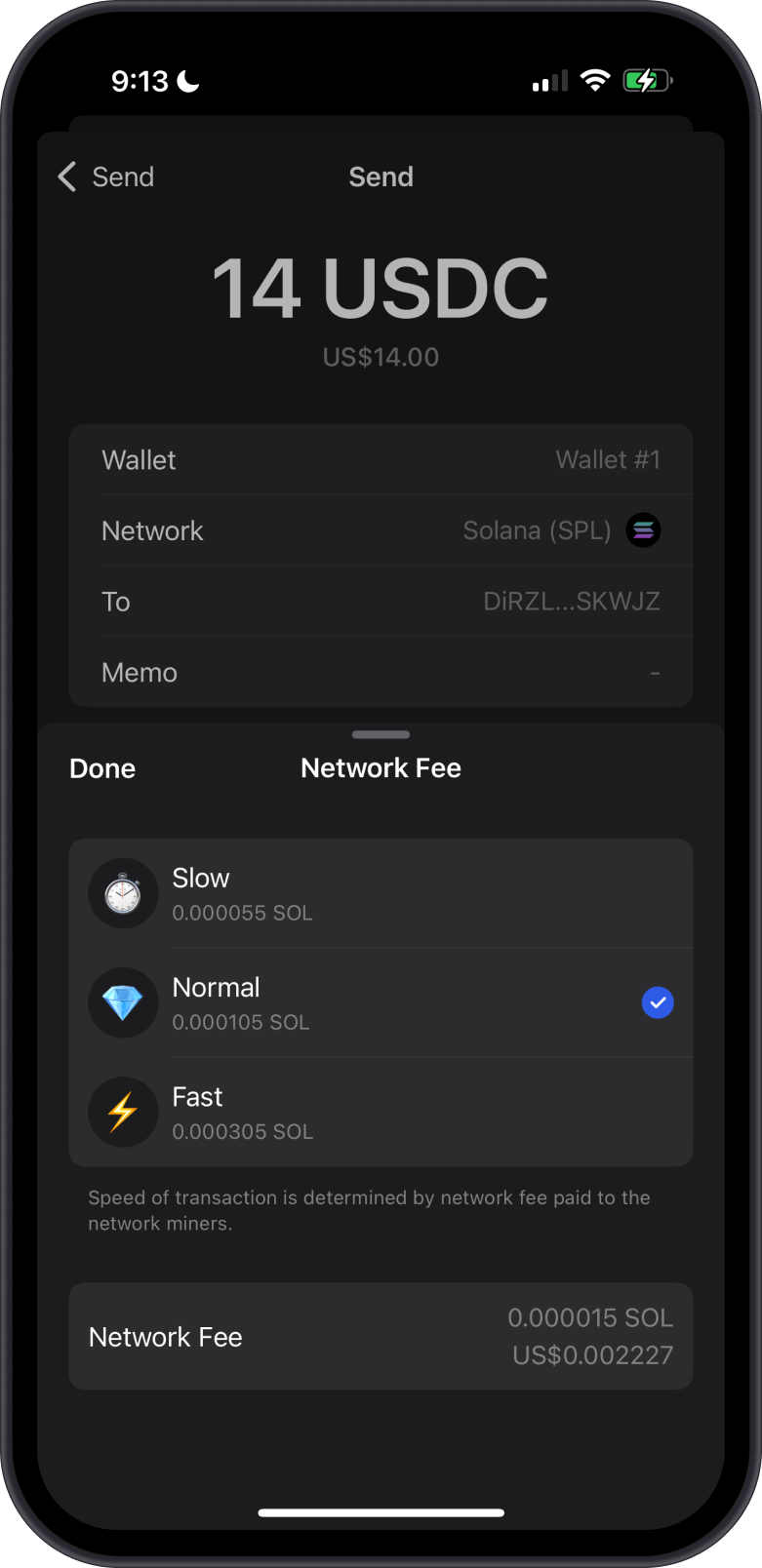
Learn more about Solana and network fees.
Does Gem Wallet Take Network Fees?
-
Gem Wallet is a non-custodial wallet, not a centralized exchange, enabling anonymous interaction with blockchains.
-
No personal information is collected from users, ensuring privacy.
-
Transactions are submitted directly to the blockchain network, with gas fees paid solely to miners or validators.
-
Gem Wallet holds no user funds and does not retain any portion of the network fees.
-
All fees are determined by the blockchain network (e.g., Ethereum gas fees) and vary based on network congestion.