Send Issues
Common Send Issues and Solutions
Here are the most common Send issues that you might encounter while using the app. Click on the issue to find the suggested solution.
Insufficient Funds
Issue:
When attempting to send cryptocurrency from your wallet, you may encounter an "insufficient funds" error. This error typically occurs when the wallet does not have enough balance to cover both the amount being sent and the associated transaction fees (often referred to as "gas fees" on networks like Ethereum).
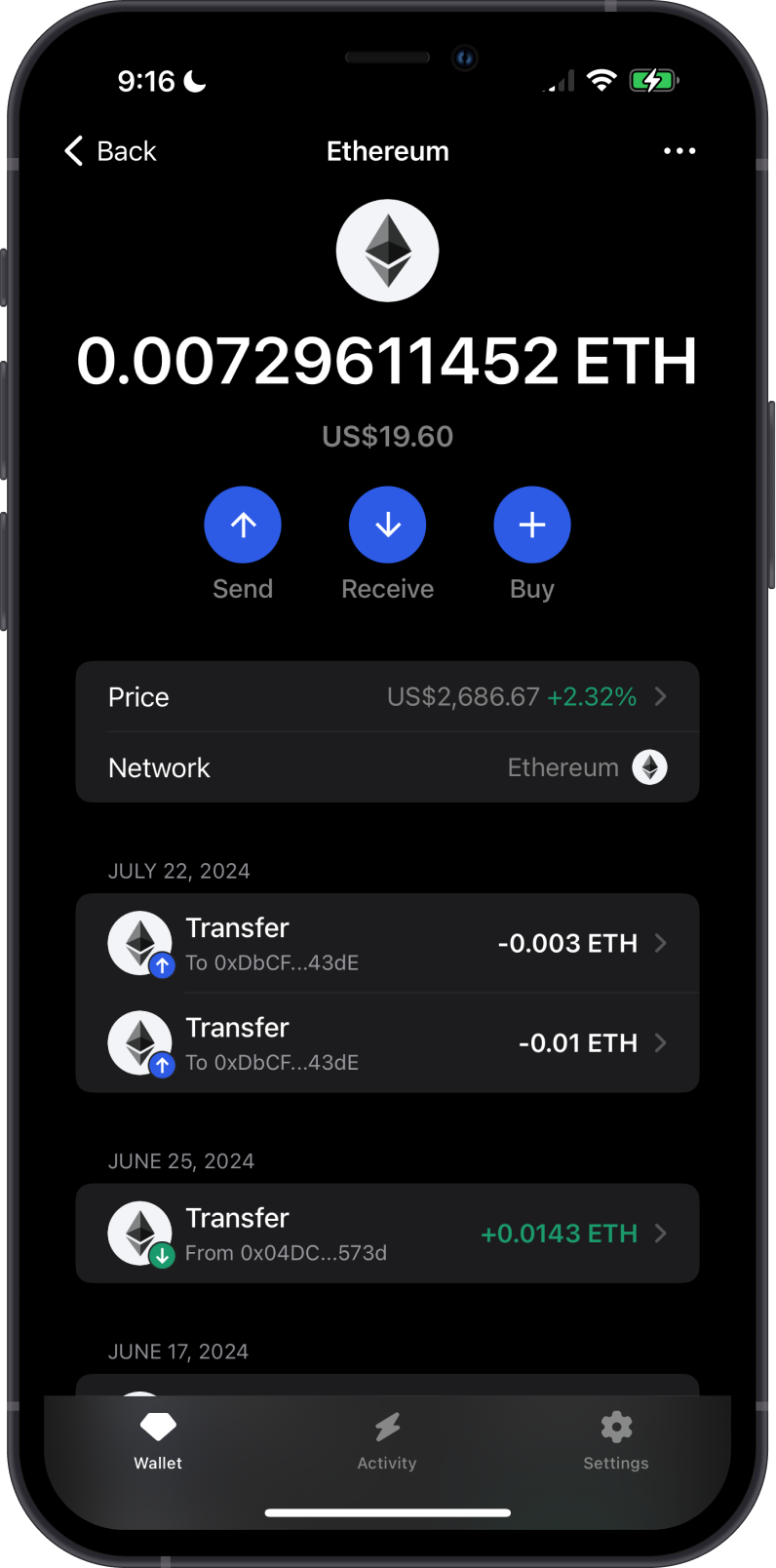
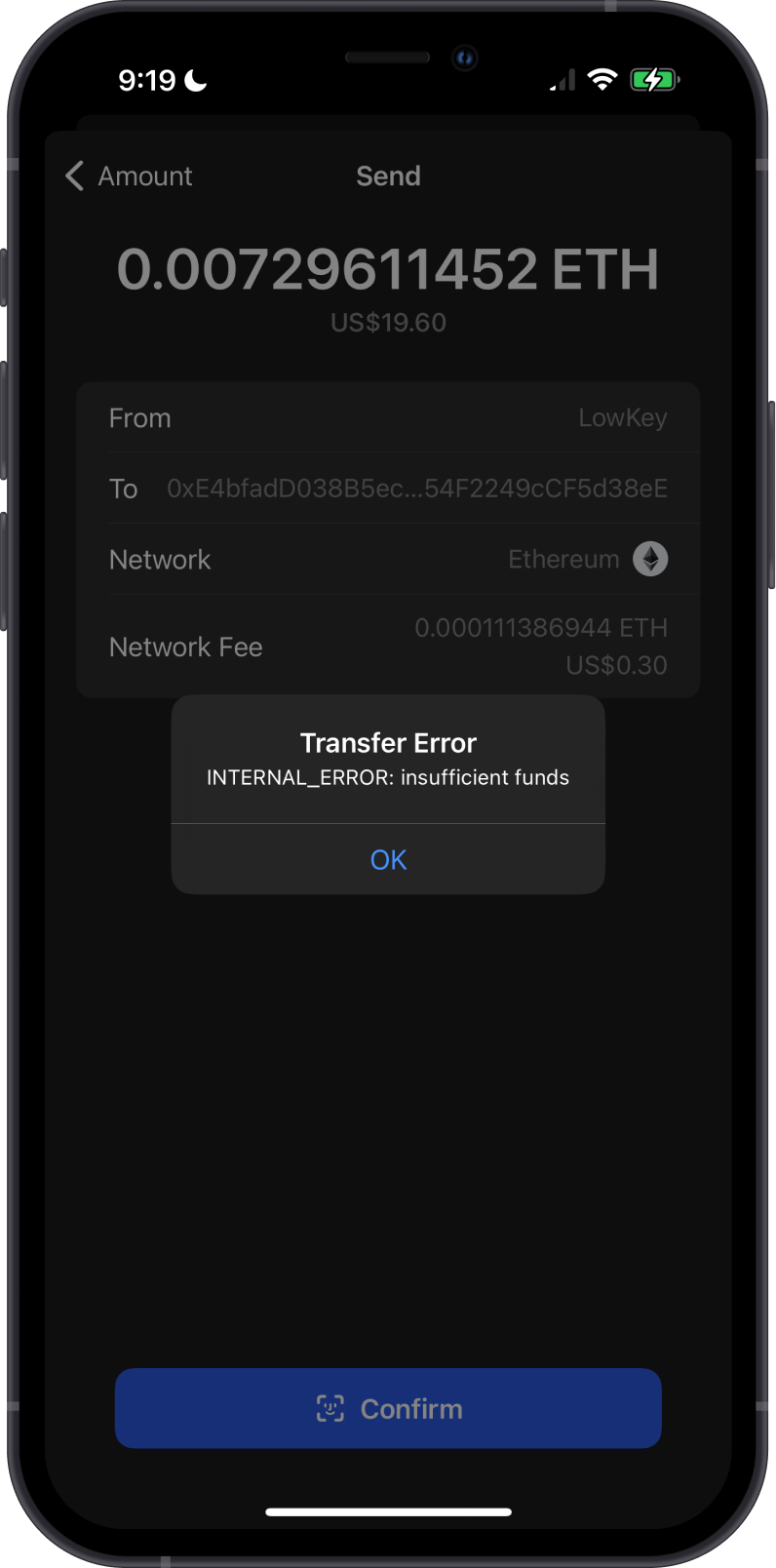
This can happen due to a few reasons:
-
Low Account Balance: The most common reason is simply not having enough cryptocurrency in the wallet. Even if you have enough to cover the amount you want to send, the transaction fee must also be accounted for.
-
High Transaction Fees: During periods of network congestion, transaction fees can spike, making it more likely that a user’s available balance is insufficient to cover both the transaction amount and the required fee.
Solution:
Ensure that you have enough cryptocurrency to cover the transaction amount plus any network fees. Check your wallet balance before initiating a transaction.
Learn more about Network Fees.
Pending Transactions
Issue:
A pending transaction occurs when a user submits a transaction to the blockchain network, but it has not yet been confirmed or included in a block. This delay can be caused by various factors and can lead to user frustration, especially if the transaction takes longer than expected to process.
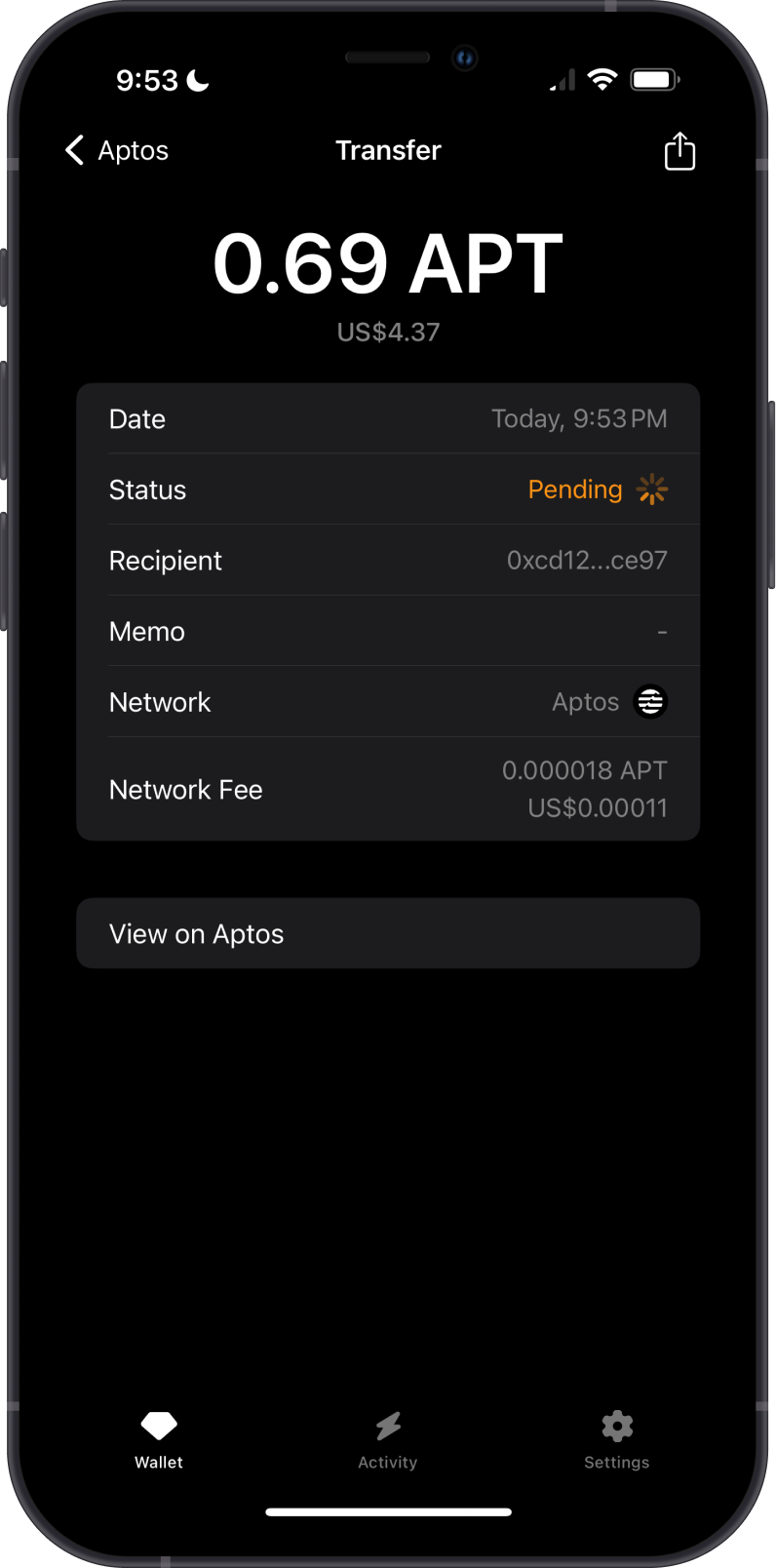
Causes of Pending Transactions:
- Network Congestion: During periods of high activity, blockchain networks can become congested with a large number of transactions waiting to be processed. This is particularly common on popular networks like Ethereum during high-demand periods.
- Low Gas Fees: Transactions are prioritized based on the gas fees attached to them. Transactions with lower fees may be delayed if miners prioritize transactions with higher fees.
Solution:
Use higher transaction fees to expedite processing. Check the transaction status on a blockchain explorer and be patient if the network is congested.
Incorrect Recipient Address
Issue:
Sending cryptocurrency to an incorrect recipient address is one of the most critical mistakes a user can make. Cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible, meaning that once the transaction is confirmed on the blockchain, it cannot be undone. If you send funds to the wrong address, you may permanently lose access to those funds.
Causes of Incorrect Recipient Address:
- Typographical Errors: Cryptocurrency addresses are long alphanumeric strings, making them prone to typos when manually entered. Even a single incorrect character can direct the funds to the wrong address.
- Copy-Paste Errors: Users often copy and paste addresses to avoid typing mistakes, but if the wrong address was copied, or if the clipboard was compromised, the wrong address could be pasted and used.
- Malicious Software: Some malicious software or browser extensions can modify the address in your clipboard to one controlled by an attacker. This happens after you copy the correct address and before you paste it.
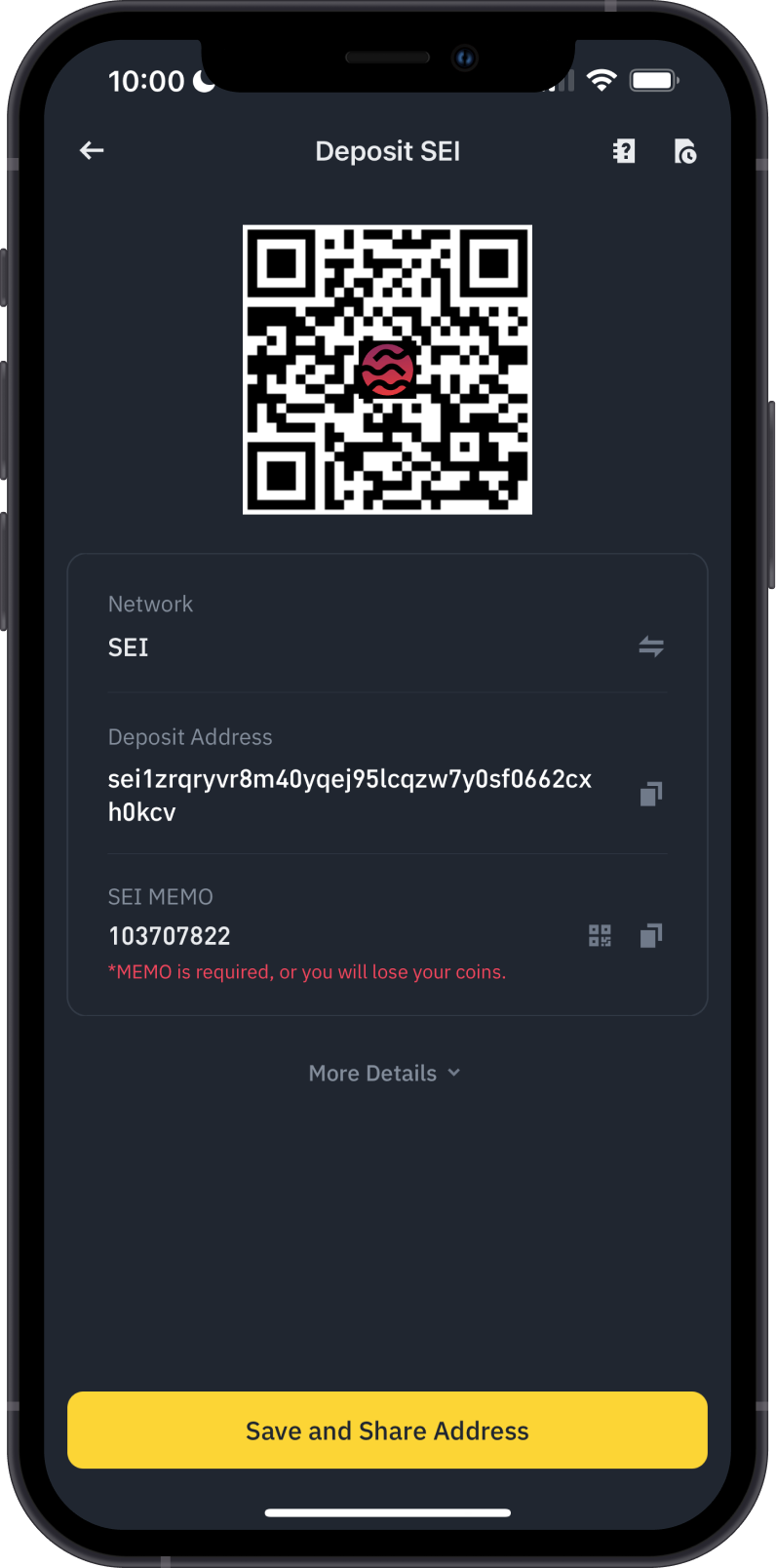
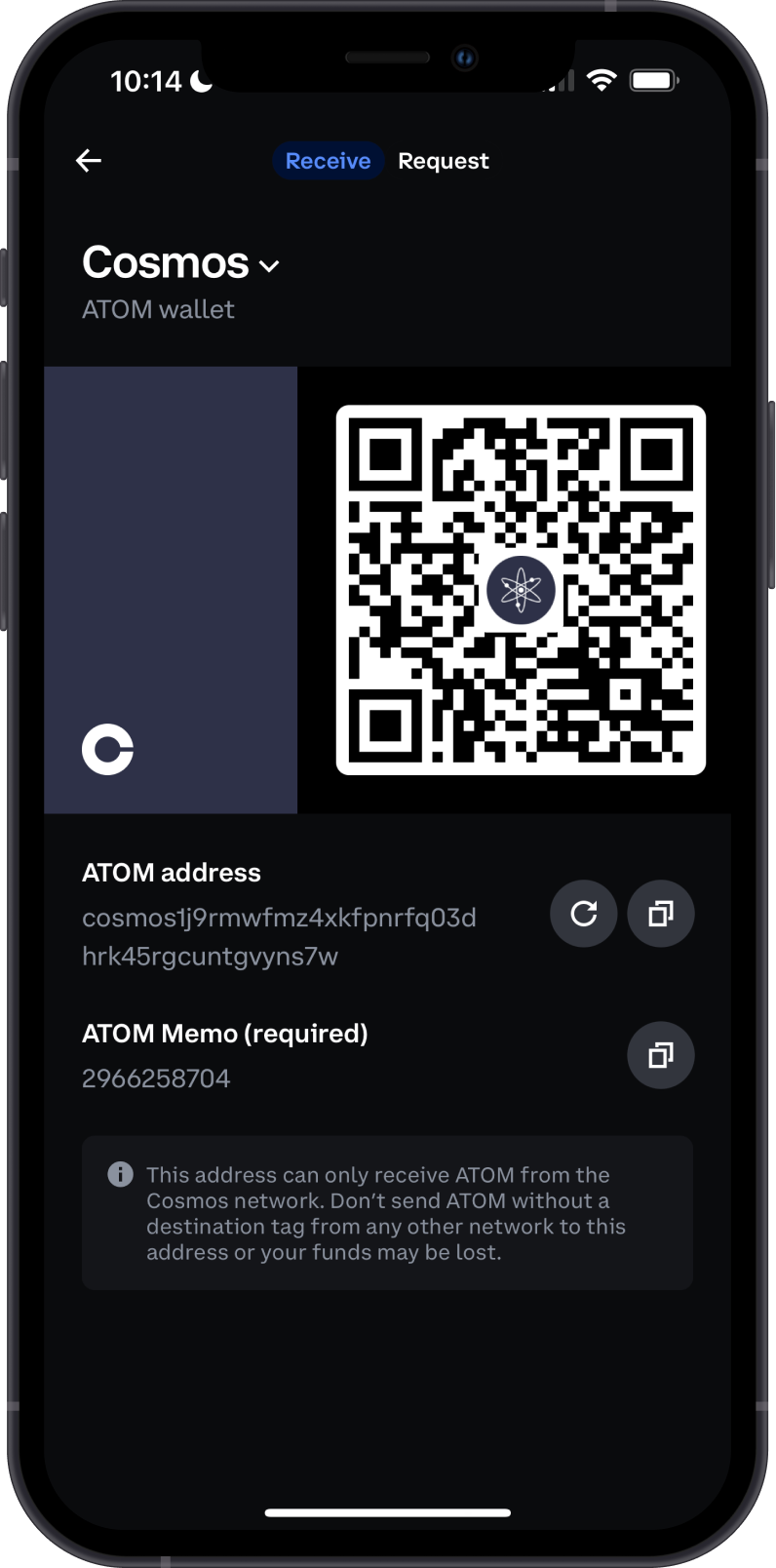
Solutions:
- Double-Check the Address: Always double-check the recipient address before confirming the transaction. This includes visually scanning the address for any typos or unusual patterns.
- Use QR Codes: Where possible, use QR codes to input addresses. This reduces the risk of typos and ensures the entire address is captured correctly. Ensure the QR code is from a trusted source and hasn’t been tampered with.
- Verify URLs: Before sending funds, make sure you are on the correct and official website of the wallet or exchange. Phishing websites often look very similar to the real ones but have minor differences in the URL.
- Send a Test Transaction: If you’re unsure, send a small amount of cryptocurrency first. This ensures that the address is correct before you send a larger amount. Wait until the test transaction is confirmed and the recipient acknowledges it before sending the full amount.
Wrong Network Selection
Issue:
Incorrect network selection occurs when users send cryptocurrency using the wrong blockchain network. For example, sending an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum network to a Binance Smart Chain (BSC) address or vice versa. This mistake can lead to the loss of funds or significant difficulties in recovering them. Since blockchain transactions are irreversible, if assets are sent on the wrong network, they might not be accessible by the intended recipient unless specific recovery steps are taken.
Common Scenarios:
-
Different Token Standards: These are token standards for Ethereum and BSC, respectively. A common mistake is sending an ERC-20 token to a BEP-20 address or a BEP-20 token to an ERC-20 address. While the addresses may look similar, the underlying blockchains are different, which can cause the tokens to become "stuck" in the wrong network.
-
Multiple Network Support: Some wallets and exchanges support multiple networks (e.g., Ethereum, BSC, Polygon). Users need to choose the correct network for their transactions. For instance, sending a token from Ethereum directly to a Polygon address without using a bridge can result in a failed transaction or lost funds.
-
Wrapped Tokens: Some tokens exist on multiple blockchains as wrapped versions (e.g., WBTC on Ethereum and Binance-Peg BTCB on BSC). Sending a wrapped token from one blockchain to another without proper conversion or bridging can cause issues.
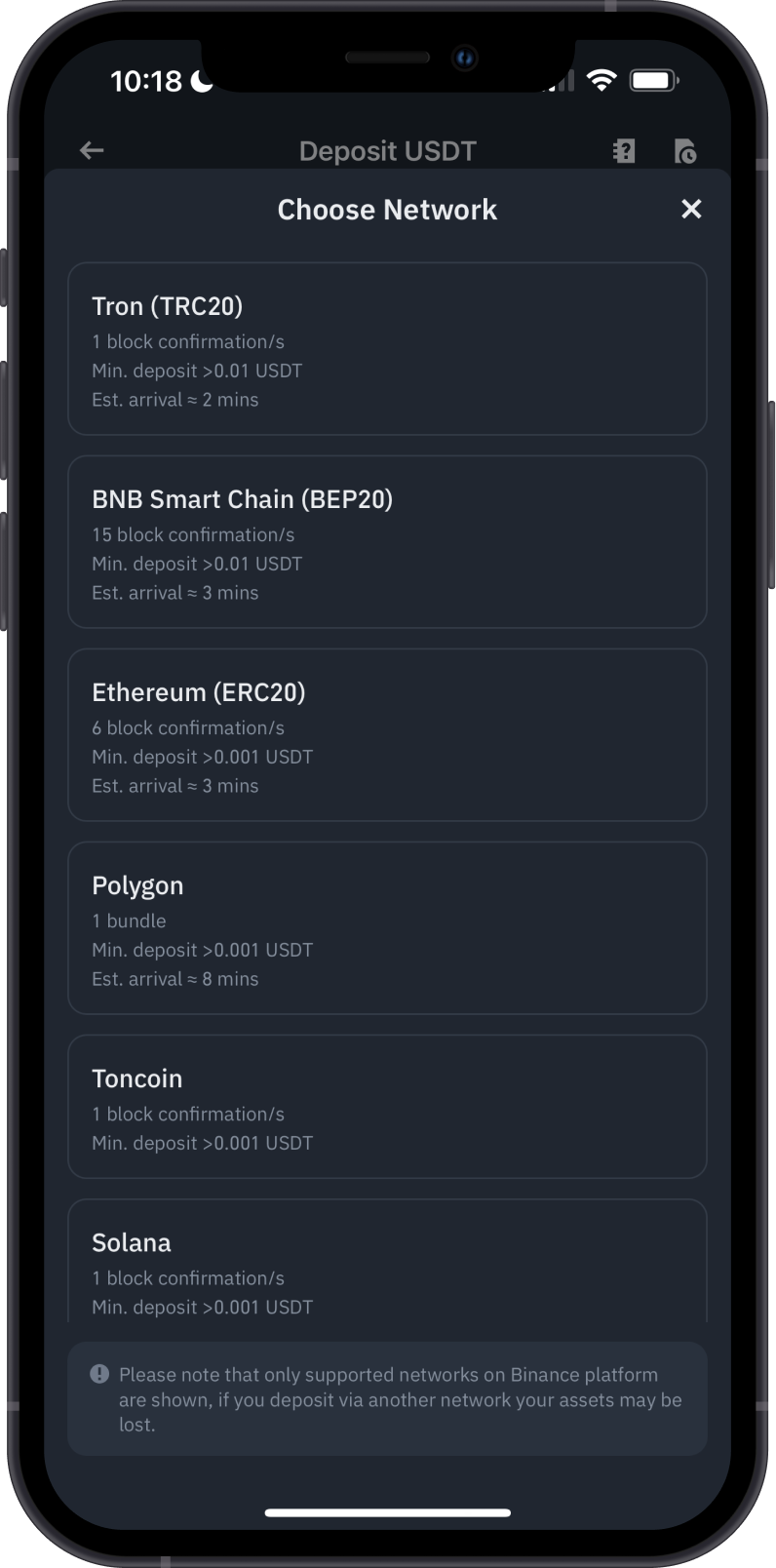
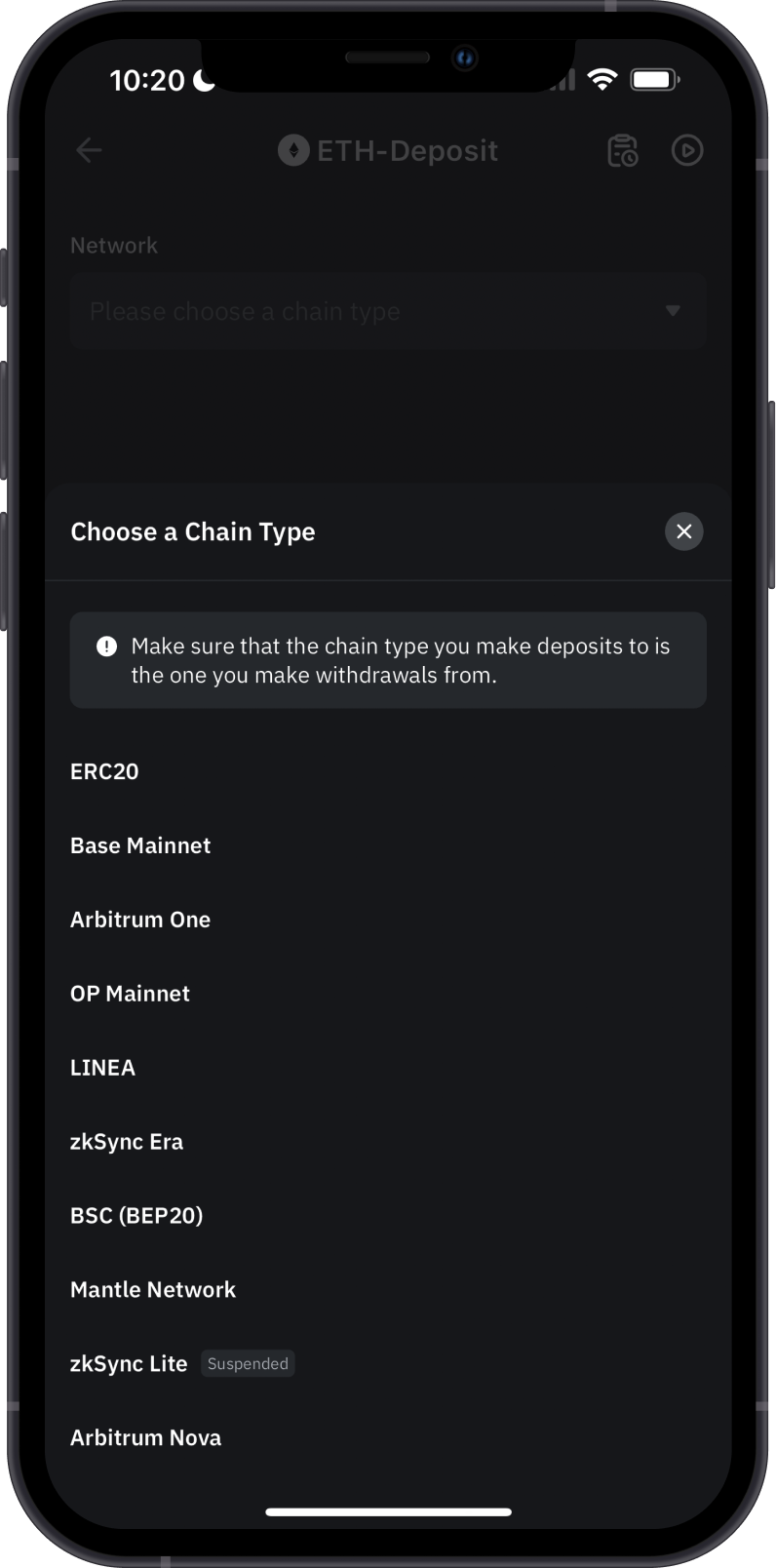
Solution:
- Double-Check Before Sending: Always ensure that both the sender and receiver are using the same network. If you're sending ERC-20 tokens, make sure the recipient address is also on the Ethereum network, not BSC or another chain. If you're transferring between networks, make sure the exchange or wallet supports both the sending and receiving networks.
- Contact Exchange Support: If you’ve made a mistake while transferring funds between different networks and can’t access your tokens, contact the support team of the wallet or exchange involved. They might be able to assist in recovering the funds, although recovery is not guaranteed.
- User Education: Understanding the differences between blockchain networks and how to transfer tokens correctly is crucial. Educate yourself or others on the distinctions between networks like Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, and others.
Other Issues or Need Further Assistance?
If you’re still facing challenges after trying these solutions or your issue is not listed above, contact Gem Wallet Support with details of your issue, including error messages, transaction IDs, and any troubleshooting steps you’ve already tried.